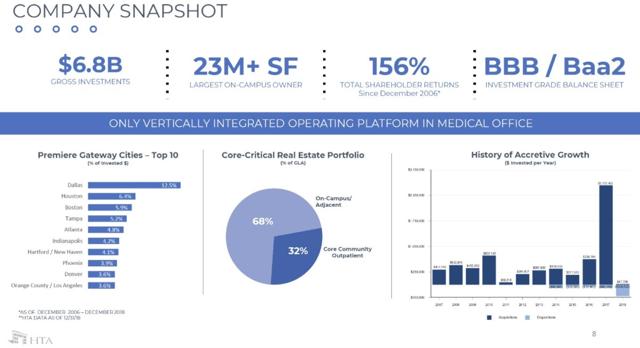
The last time the Super Bowl came to Miami, the football stadium on the edge of the Everglades and just off the turnpike was surrounded by asphalt and dirt parking lots.
Miami-Dade County had 20% fewer apartments and 23% fewer available hotel rooms during the championship game in 2010, when Airbnb and ride-hailing companies such as Uber were in their infancy. Brightline, the commuter train service renamed Virgin Trains USA that connects Miami with West Palm Beach and Fort Lauderdale, didn’t exist. All those factors are expected to play major roles this weekend as Miami hosts the Super Bowl for a record 11th time, attracting more than 200,000 people to a region with a skyline that has changed dramatically.
“If you were here 10 years ago and came back, you’ll find that this city is completely different,” Miami-Dade County Mayor Carlos Gimenez said.
North of downtown, once-distressed neighborhoods such as Allapattah and Little Haiti are attracting new development that appeals to millennials who want to live close to where they work. One of the trendiest areas of Miami is Wynwood, a former industrial and garment district now drawing offices, retail and residential. Tour buses regularly pass through Wynwood, allowing visitors to snap selfies among the spray-painted graffiti that adorns many of the buildings in the rollicking arts district.
“Miami has become more of an urban place where people live and play now,” said Rodney Barreto, chairman of the Miami Super Bowl Host Committee. “It wasn’t that 10 years ago. Heck, at 6 or 7 o’clock at night you couldn’t find anybody downtown. Now at 11 o’clock at night, people are walking their dogs.”
In the past 10 years, close to 30,000 new apartments have been built across Miami-Dade County, helping make it the U.S. capital for rentals as a percentage of inventory, according to CoStar data. The market has added 11,000 more hotel rooms, not including thousands of new beds now available through home-sharing giant Airbnb. Scores of luxury condominium towers are sprouting up in downtown Miami, including one that has an amenity deck that can be transformed into a skyport for flying cars and another with a robot concierge service.
The 65,000-seat Hard Rock Stadium is now the new home of the Miami Open tennis tournament and has attracted soccer, concerts and other events. Last year, ground was broken on a $135 million Dolphins training facility next to the stadium. And gondolas were installed that will make their debut on Super Bowl Sunday, giving fans an aerial view of the pregame festivities.
“It’s definitely a different town, and we’re going to be really proud to show it off, for sure,” Barreto said.
The Feb. 2 game at Hard Rock Stadium between the Kansas City Chiefs and San Francisco 49ers is expected to generate an estimated economic impact in excess of $400 million. Hotels in the Miami area are projected to break all-time highs for average daily rate and revenue per available room, two industry standard measurements, according to figures from STR, a travel industry data and analytics firm owned by CoStar Group, the parent company of CoStar News.
Making the Pitch
NFL owners voted in 2016 to award South Florida this year’s Super Bowl, a game that marks the league’s 100th season. They were sold after listening to a pitch from Miami Dolphins owner and Hudson Yards developer Stephen Ross about hundreds of millions of dollars he spent to renovate the aging Hard Rock Stadium in Miami Gardens, on the edge of the Everglades northwest of downtown Miami.
At the time, the Dolphins and Barreto said the region’s bid, which topped 550 pages, included a budget of cash and incentives valued at more than $40 million. Barreto now declines to discuss specifics of the bid, saying parts of it eventually will be made public.
Miami, the nation’s seventh-largest metropolitan area, is a preferred destination for the Super Bowl because of its size and the consistently warm weather, notwithstanding the Super Bowl in 2007, but even then fans found it strangely appropriate that halftime performer Prince sang his hit song “Purple Rain” in the rain.
Meanwhile, the matchups in Miami have been among the most memorable in league history.
In the second of five Super Bowls played at the Orange Bowl in Miami, New York Jets quarterback Joe Namath famously guaranteed victory over the Baltimore Colts in 1969, a huge upset that led to the merger of the NFL and the American Football League.
Twenty years later, in a new stadium privately funded by Dolphins founding owner Joe Robbie, San Francisco 49ers quarterback Joe Montana jokingly pointed out actor John Candy in the crowd to his teammates before leading them on a last-second drive to beat the Cincinnati Bengals.
A decade ago, the New Orleans Saints outlasted the now Indianapolis Colts with the help of a risky onside kick to open the second half, delivering the Big Easy’s first title, 4 1/2 years after the city was devastated by Hurricane Katrina.
But not long after the Saints beat the Colts in February 2010, NFL Commissioner Roger Goodell delivered a stark message to Ross and other officials hoping to schedule another Super Bowl at Hard Rock.
“The commissioner was very adamant and very loud about we would not get another Super Bowl until we made renovations,” Barreto told CoStar News.
Stadium Improvement Process
Ross first sought public money to renovate the stadium that opened in 1987, though that effort hit a political wall. In 2014, he struck a deal with Miami-Dade to pay for the upgrades himself in exchange for bonus payments to the Dolphins for hosting the Super Bowl and other events.
The phased stadium improvements brought new seats, two new concourses, new suites, four high-definition video boards and a canopy that shades 92% of the fans. The cost: more than $550 million.
Ross’ total investment at Hard Rock Stadium now tops $700 million, noted Tom Garfinkel, president and CEO of the Dolphins and member of the Miami Super Bowl Host Committee.
“It’s a testament to Steve Ross’ commitment,” Garfinkel said in an interview. “The stadium has become a global entertainment destination.”
The NFL seems impressed.
Senior Director of Event Planning Eric Finkelstein, whose crew of 6,000 workers has been in South Florida since Jan. 2 preparing for the Super Bowl, said the new canopy allows the league to introduce surprises for fans during the championship game.
“To us, it feels like a brand new building because of how much has changed,” said Finkelstein, who is overseeing his 21st Super Bowl.
NFL owners typically vote to award the game to cities with warm weather or domed stadiums. Teams that agree to build stadiums, as the Los Angeles Rams are doing, have a good chance of eventually hosting the Super Bowl. Tampa, Florida, doesn’t have a new stadium, but NFL owners voted to move the Super Bowl there in February 2021 from Inglewood, California, because of construction delays at the Los Angeles Rams’ SoFi Stadium. It will be the fifth time Tampa has hosted the game. The big game heads to SoFi Stadium in the Los Angeles area in 2022.
Local civic and business leaders insist they aren’t taking for granted the impact of the game on South Florida, no matter how many times it has been played here.
“We have the attention and the focus of the world,” Miami Mayor Francis Suarez said.
Barreto has signed paperwork to allow South Florida to compete for the Super Bowl in any year from 2025 to 2030. He was watching on television Wednesday when Goodell, speaking at his state of the league press conference, praised local officials and indicated the game likely will return to Hard Rock Stadium.
“We’re ecstatic,” Barreto said. “I believe they like Miami. We’re experienced, and we know how to work with them.”
Source: CoStar